728x90
스프링 AOP ( Aspect Oriented Programming )
- AOP는 Aspect Oriented Programming의 약자로 관점 지향 프로그래밍이라고 불린다. 관점 지향은 쉽게 말해 어떤 로직을 기준으로 핵심적인 관점, 부가적인 관점으로 나누어서 보고 그 관점을 기준으로 각각 모듈화하겠다는 것이다. 여기서 모듈화란 어떤 공통된 로직이나 기능을 하나의 단위로 묶는 것을 말한다.
- 예로들어 핵심적인 관점은 결국 우리가 적용하고자 하는 핵심 비즈니스 로직이 된다. 또한 부가적인 관점은 핵심 로직을 실행하기 위해서 행해지는 데이터베이스 연결, 로깅, 파일 입출력 등을 예로 들 수 있다.
- AOP에서 각 관점을 기준으로 로직을 모듈화한다는 것은 코드들을 부분적으로 나누어서 모듈화하겠다는 의미다. 이때, 소스 코드상에서 다른 부분에 계속 반복해서 쓰는 코드들을 발견할 수 있는 데 이것을 흩어진 관심사 (Crosscutting Concerns)라 부른다.
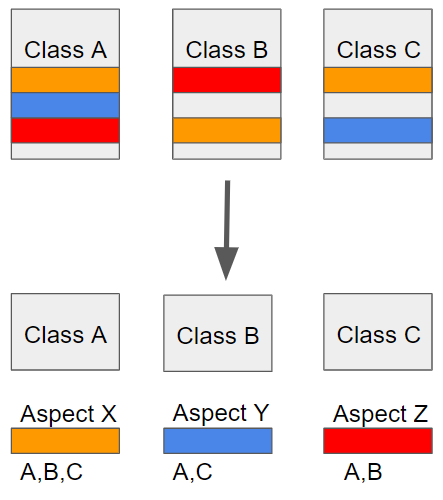
- 위와 같이 흩어진 관심사를 Aspect로 모듈화하고 핵심적인 비즈니스 로직에서 분리하여 재사용하겠다는 것이 AOP의 취지다.
AOP 주요 개념
- Aspect : 위에서 설명한 흩어진 관심사를 모듈화 한 것. 주로 부가기능을 모듈화함.
- Target : Aspect를 적용하는 곳 (클래스, 메서드 .. )
- Advice : 실질적으로 어떤 일을 해야할 지에 대한 것, 실질적인 부가기능을 담은 구현체
- JointPoint : Advice가 적용될 위치, 끼어들 수 있는 지점. 메서드 진입 지점, 생성자 호출 시점, 필드에서 값을 꺼내올 때 등 다양한 시점에 적용가능
- PointCut : JointPoint의 상세한 스펙을 정의한 것. 'A란 메서드의 진입 시점에 호출할 것'과 같이 더욱 구체적으로 Advice가 실행될 지점을 정할 수 있음
스프링 AOP 특징
- 프록시 패턴 기반의 AOP 구현체, 프록시 객체를 쓰는 이유는 접근 제어 및 부가기능을 추가하기 위해서임
- 스프링 빈에만 AOP를 적용 가능
- 모든 AOP 기능을 제공하는 것이 아닌 스프링 IoC와 연동하여 엔터프라이즈 애플리케이션에서 가장 흔한 문제(중복코드, 프록시 클래스 작성의 번거로움, 객체들 간 관계 복잡도 증가 ...)에 대한 해결책을 지원하는 것이 목적
스프링 AOP : @AOP
스프링 @AOP를 사용하기 위해서는 다음과 같은 의존성을 추가해야 한다.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
다음에는 아래와 같이 @Aspect 어노테이션을 붙여 이 클래스가 Aspect를 나타내는 클래스라는 것을 명시하고 @Component를 붙여 스프링 빈으로 등록한다.
@Component
@Aspect
public class PerfAspect {
@Around("execution(* com.saelobi..*.EventService.*(..))")
public Object logPerf(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable{
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
Object retVal = pjp.proceed(); // 메서드 호출 자체를 감쌈
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() - begin);
return retVal;
}
}
- @Around 어노테이션은 타겟 메서드를 감싸서 특정 Advice를 실행한다는 의미이다. 위 코드의 Advice는 타겟 메서드가 실행된 시간을 측정하기 위한 로직을 구현하였다. 추가적으로 execution(* com.saelobi..*.EventService.*(..))가 의미하는 바는 com.saelobi 아래의 패키지 경로의 EventService 객체의 모든 메서드에 이 Aspect를 적용하겠다는 의미다.
public interface EventService {
void createEvent();
void publishEvent();
void deleteEvent();
}@Component
public class SimpleEventService implements EventService {
@Override
public void createEvent() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Created an event");
}
@Override
public void publishEvent() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();;
}
System.out.println("Published an event");
}
public void deleteEvent() {
System.out.println("Delete an event");
}
}@Service
public class AppRunner implements ApplicationRunner {
@Autowired
EventService eventService;
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
eventService.createEvent();
eventService.publishEvent();
eventService.deleteEvent();
}
}Created an event
1003
Published an event
1000
Delete an event
0
- 또한 경로지정 방식말고 특정 어노테이션이 붙은 포인트에 해당 Aspect를 실행할 수 있는 기능도 제공한다.
@Component
@Aspect
public class PerfAspect {
@Around("@annotation(PerLogging)")
public Object logPerf(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable{
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
Object retVal = pjp.proceed(); // 메서드 호출 자체를 감쌈
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() - begin);
return retVal;
}
}@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.CLASS)
public @interface PerLogging {
}@Component
public class SimpleEventService implements EventService {
@PerLogging
@Override
public void createEvent() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Created an event");
}
@Override
public void publishEvent() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();;
}
System.out.println("Published an event");
}
@PerLogging
@Override
public void deleteEvent() {
System.out.println("Delete an event");
}
}Created an event
1003
Published an event
Delete an event
0위 출력 결과에서 @PerLogging 어노테이션이 붙은 메서드만 Aspect가 적용된 것을 볼 수 있다.
마찬가지로 스프링 빈의 모든 메서드에 적용할 수 있는 기능도 제공한다.
@Component
@Aspect
public class PerfAspect {
@Around("bean(simpleEventService)")
public Object logPerf(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable{
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
Object retVal = pjp.proceed(); // 메서드 호출 자체를 감쌈
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() - begin);
return retVal;
}
}@Component
public class SimpleEventService implements EventService {
@Override
public void createEvent() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Created an event");
}
@Override
public void publishEvent() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();;
}
System.out.println("Published an event");
}
@Override
public void deleteEvent() {
System.out.println("Delete an event");
}
}@Service
public class AppRunner implements ApplicationRunner {
@Autowired
EventService eventService;
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
eventService.createEvent();
eventService.publishEvent();
eventService.deleteEvent();
} }Created an event
1002
Published an event
1001
Delete an event
0
위 출력결과로 SimpleEventService의 모든 메서드에 해당 Aspect가 추가된 것을 알 수 있다.
이 밖에도 @Around 외에 타겟 메서드의 Aspect 실행 시점을 지정할 수 있는 어노테이션이 있다.
@Before (이전) : 어드바이스 타겟 메소드가 호출되기 전에 어드바이스 기능을 수행
@After (이후) : 타겟 메소드의 결과에 관계없이(즉 성공, 예외 관계없이) 타겟 메소드가 완료 되면 어드바이스 기능을 수행
@AfterReturning (정상적 반환 이후)타겟 메소드가 성공적으로 결과값을 반환 후에 어드바이스 기능을 수행
@AfterThrowing (예외 발생 이후) : 타겟 메소드가 수행 중 예외를 던지게 되면 어드바이스 기능을 수행
@Around (메소드 실행 전후) : 어드바이스가 타겟 메소드를 감싸서 타겟 메소드 호출전과 후에 어드바이스 기능을 수행
출처 : https://engkimbs.tistory.com/746
[Spring] 스프링 AOP (Spring AOP) 총정리 : 개념, 프록시 기반 AOP, @AOP
| 스프링 AOP ( Aspect Oriented Programming ) AOP는 Aspect Oriented Programming의 약자로 관점 지향 프로그래밍이라고 불린다. 관점 지향은 쉽게 말해 어떤 로직을 기준으로 핵심적인 관점, 부가적인 관점으로
engkimbs.tistory.com
728x90
'Spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
| @Controller와 @RestController의 차이점 (0) | 2023.03.05 |
|---|---|
| PointCut 표현식 정리 (0) | 2023.03.03 |
| SpringBoot + Mybatis 연동하기 (0) | 2023.01.12 |
| SpringBoot + JPA 멀티 연동하기 (0) | 2023.01.12 |
| RestTemplate과 WebClient(feat. 서버 간 데이터 주고 받기) (0) | 2022.12.02 |